Value-based healthcare (VBHC) represents a promising approach for achieving better outcomes at a lower cost and has the potential to transform how healthcare is delivered and managed in the years to come. The VBHC model constantly puts an emphasis on outcomes and costs to deliver the best value for the patient and the healthcare provider. It seeks to measure the quality of care by assessing the costs and health outcomes associated with a particular treatment or procedure. This system of care encourages providers to focus on providing cost-effective and quality care.
Measuring costs accurately is critical to have a better value in healthcare. All micro and macro cost components of treating patients throughout their care cycle are not currently captured by the legacy healthcare accounting systems along with respective health outcomes. Therefore, developing a method to assess healthcare expenses and corresponding results is vital.
Time-driven activity-based costing (TDABC) is an improved form of activity-based costing (ABC) that uses cost drivers to link activities to resource costs. It can be used to identify the cost of each activity within a healthcare system, providing a more accurate analysis of how resources are used. It also helps to understand (1) the true costs of providing services, (2) develop strategies to reduce costs, and (3) increase efficiency. TDABC can also provide guidelines for making informed decisions about resource allocations and the pricing of services. By providing more accurate cost information, TDABC can help healthcare organizations to manage costs better and improve patient outcomes.
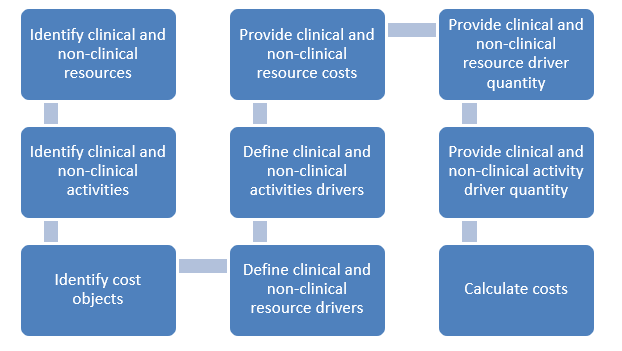
TDABC is a data-driven approach to healthcare delivery that can be used to optimize the cost and effectiveness of care. To achieve the goal of value-based care, healthcare organizations must first understand the processes they use to deliver care, the resources they consume, and the outcomes they achieve. This requires a detailed understanding of healthcare delivery processes, activities, and resources. Once this understanding has been achieved, TDABC can be used to identify areas of inefficiency and develop strategies for improvement. Salesforce Health Cloud is very helpful in utilizing the data to measure cost and corresponding outcomes.
Usually, the total cost of healthcare can be categorized into two components, i.e., direct costs and indirect costs.
- Direct cost – Directly assigned to a service or procedure.
Examples – clinician labor, Implants, Laboratory testing, Prescription medications, consumables, etc.)
- Indirect cost – Fixed/periodic costs of support resources necessary to supply a service/procedure.
Examples – non-clinical salaries such as maintenance and housekeeping, Hospital administration, sterilization of equipment, etc.)
Standard objects available in Salesforce Health Cloud, like PatientMedicalProcedure, WorkProcedure, and WorkProcedureStep, can be utilized to calculate the cost via Time-driven activity-based approach.
- WorkProcedure represents information about a procedure or process part of a program.
- WorkProcedureStep is the work type that is part of a work procedure.
- PatientMedicalProcedure represents detailed information about a healthcare procedure the patient has undergone, is undergoing, or will undergo.
Furthermore, Advanced Therapy Management, which helps streamline complex procedures, can enable the management of costs in complex scenarios with some customization.
TDABC can give healthcare managers a deeper understanding of the cost associated with care delivery. With the data gathered through TDABC, healthcare managers can identify areas of inefficiency and waste. This can then be used to inform decisions about reducing costs associated with care delivery. Now a day, many surgeons and hospitals are participating in bundled payments to reduce costs and identify ways to improve the efficiency of care delivery.
Salesforce Health Cloud can certainly be helpful in monitoring healthcare costs and health outcomes by implementing approaches like TDABC.
#healthcare #salesforce #healthcloud #valuebasedcare
References
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32540239/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7000080/
https://help.salesforce.com/s/articleView?id=sf.healthcare_admin.htm&type=5